improve cytotoxic response
There are very few adjuvants, especially available for Research and Development, that can substantially change the cytotoxic immune response. Meanwhile, it is often very critical to know whether the reason for poor cytotoxic immune response is the vaccine itself or poor antigen. The proposed adjuvants, developed for use in human and animal vaccines are now made available via Aptum for researchers worldwide. They allow substantially improve the immune response in vitro and in in vivo.
The key infomration on ImmAccel-T adjuvants:
-
the adjuants are small (<2 kD) peptides that modulate the antigen processing of antigen in dendritic and other antigen-presenting cells
-
they are non toxic (belong to compounds of the lowest toxicity (group VI), with 10.000 times the active dose still showing no acute toxic affects
-
They effectively boost specific CTL responses in vitro and in vivo
-
The adjuvants do not influence response of CTLs to APCs with externally loaded peptides; the processing of antigen (including cross-presentation) is important.
-
For antigen T4 at high concentrations the non-specific stimulation of T-cell proliferation proliferation may be observed
Increase of cytotoxic response in vitro by ImmAccel-T adjuvants
ImmAccel-T adjuvants
This group of safe, non-toxic peptide adjuvants was developed to potentate the response to vaccines of humans and animals, and some of theme are already included into commercial vaccines.
To illustrate the effect of ImmAccel-T adjuvants we present here the results of the latter on proliferative response of specific T-cells int he presence of Dendritic cells processing and presenting the antigen and adjuvant.
T-cells, isolated from the OT-1 transgenic mice that express on T-cells a TCR specific to MHC class I epitope of ovalbumin, were added to syngenic DCs (moncyte-derived) that processed and presented ovalbumin. The antigen was added to the test viasl in different concentrations. The proliferative response of CTLs was measured by thymidine incorporation. The experiment was performed in the presence or absence of adjuvant in standard concentration (10 mcg in this expreiment).
As can be seen from the presented results (on the left), the presence of adjuvant increased the level of response to a cross-presented antigen.
The effect was especially evident when the dose of antigen was the limiting factor: at lower concentrations of the antigen, the adjuvants T1 and T4 amplified the response to 10-15 times. Even stronger boost of the response is possible at higher concentrations of T4 (up to 100 times, the result not shown).
The experimets were performed in the laboratory of Prof. G.Kraal, Fres University of Amsterdam, the Netherlands.

Proliferative resposne of OT-1 CTLs at various doses of antigen


Ordering Information
Increase of cytotoxic response in vivo by ImmAccel-T adjuvants
ADJUVANT T1/T4 DATA SHEET
ADJUVANT T1/T4 MSDS
ADJUVANT T1/T4 SAFETY FOR ANIMALS INFORMATION

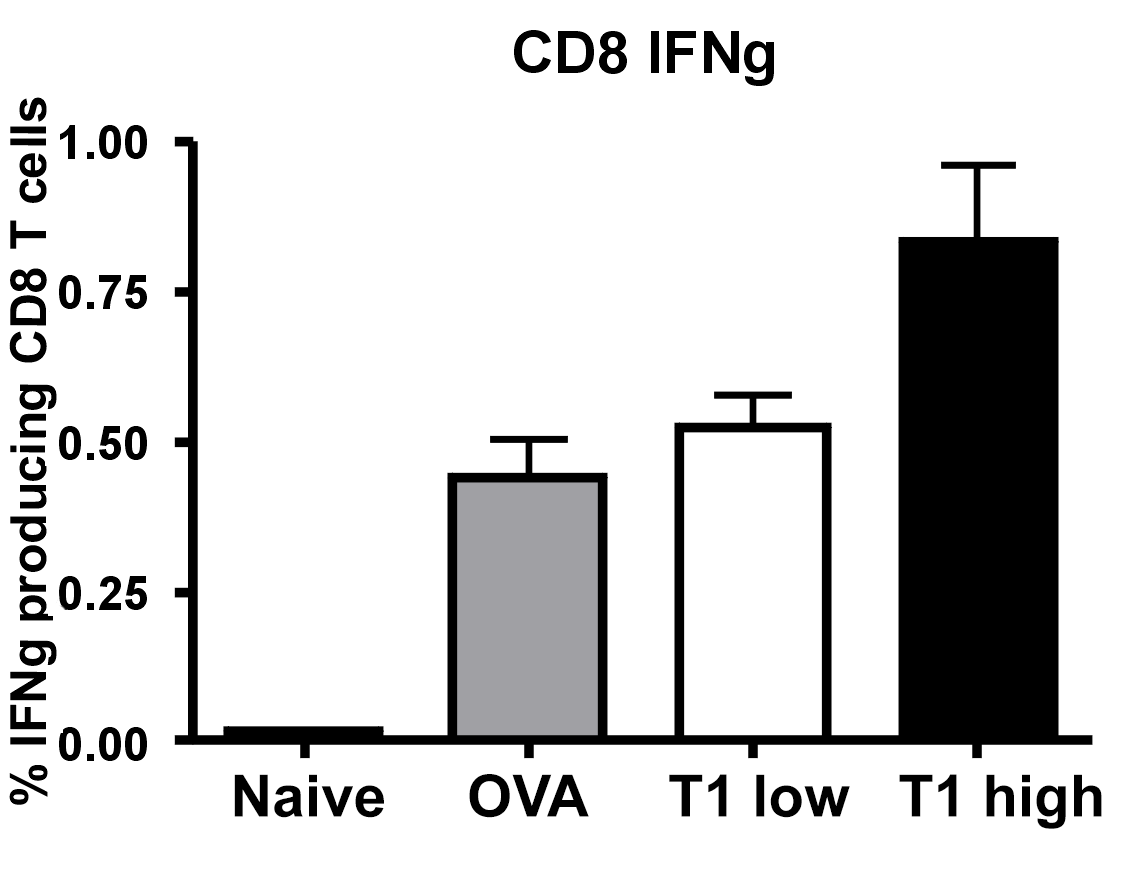
Mice were immunized with the antigen (OVA) in the tail base in incomplete Freunds adjuvant in the presence of ImmAccel T1. Six days later the animals received a mixture of spleen cells that had been labelled with a high or a low dose of CFSE to be able to distinguish them by flow cytometry. The cells that had been labelled with the high dose of CFSE were labelled with an OVA derived peptide that binds to mouse MHC class I. These cells, thereby, form target cells that can be killed by CTL that have developed in response to the OVA immunization.
Seven hours after injection the mice were killed, their spleens were removed and single cell suspensions were prepared. These were analysed by flow cytometry for the percentage of CFSE labelled cells of low and high intensity. The relative loss of OVA-peptide labelled CSFE high cells compared to CSFE low cells is a measure of functional CTL activity in the animal.
In addition to these measurements the spleen cells were cultured for 24h in the presence of OVA and analysed for the presence of CD8 positive IFN-gamma producing T cells. This is a direct measure of the number of CTLs, generated in the animals.


